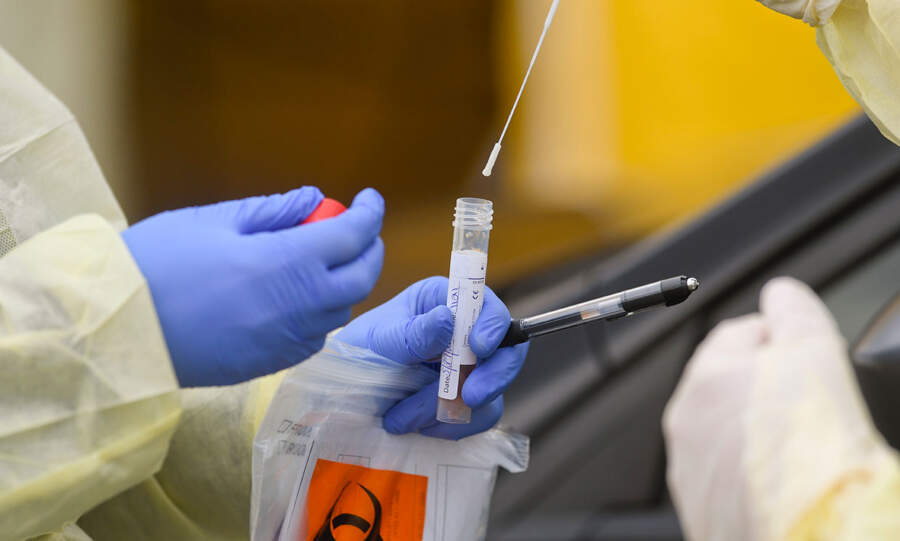
Have you heard of the FlowFlex antigen rapid COVID-19 test? If you have, how much do you know about the FlowFlex COVID-19 test accuracy and the accuracy of other coronavirus tests?
Since the pandemic started, medical experts worldwide have developed new technologies to help in the early and accurate detection of COVID-19 among symptomatic and asymptomatic patients.
These technologies work differently to achieve a common goal and use techniques that include PCR, rapid diagnostics, and serological assays. Unfortunately, very few people outside the medical field know how these tests operate. We, therefore, came up with this article to highlight the ins and outs of these COVID-19 testing gadgets.
History Behind Coronavirus Tests
When COVID-19 was first discovered, many of the current testing devices we are using were still inexistent. During that period, patients could only get tested via an assay that relied on the RT-PCR form of testing, an abbreviation for Reverse Transcriptase Polymerase Chain Reaction.
RT-PCR was a testing method that isolated and amplified SARS-CoV-2’s viral code, which is the virus that causes COVID-19. Although these tests were accurate and reliable, it took a lot of resources and time before the test results became ready. However, things started changing for the better as more research was conducted on COVID-19 which led to the introduction of newer, faster, and more accurate forms of testing.
How Samples for Testing Are Collected
There is a common method that dictates how a COVID-19 sample can be collected for testing. Although these methods may change in the future, the one currently being used globally involves the collection of samples from the upper respiratory tract. This was chosen over other sample collection methods as scientists found the area to be the most populated with the virus.
Sample Analyzation
Upon completion of the first phase, the next thing we’ll do is have the sample analyzed for traces of COVID-19. Again, this process will vary depending on the method of testing used and how the sample was collected.
RT-PCR Test
An RT-PCR Test can only be done by trained technicians who take the samples to an offsite lab for analysis. The viral RNA is first isolated and extracted from the sample cells during analysis. After completion, the sample is amplified and broken down repeatedly to increase its viral DNA, which can accumulate to millions or even billions after completion.
RT-PCR testing is time-consuming since analysis and testing are conducted on different sites, which contributes to the delay in result transmission. As a result, patients will sometimes have to wait for hours, days, or longer before getting their results back, especially if there is a backlog.
Rapid Diagnostics
Rapid diagnostics testing uitlizes a new technique called isothermal amplification. The device is accurate and can detect viruses in the patients’ antigens without going through the lengthy analysis process that samples are subjected to during PCR tests. As a result, patients can expect their COVID-19 test results to come out in minutes.
Blood Test
This form of testing is also called antibody testing, immunoassay or serological testing and works by identifying antibodies in the sample collected. Our body contains proteins called immunoglobulins, which only exist inside after an immune response to coronavirus infection. Blood testing uses part of our body’s viral code to search for these antibodies to confirm the presence of COVID-19.
It’s worth noting that these new forms of testing were not meant to replace the existing ones but rather to supplement them or serve as alternatives.
Conclusion
The rapid spread of COVID-19 has led medical experts and scientists worldwide to work towards a common goal: stopping the spread of coronavirus. With research and testing, these scientists were soon able to invent new and modern testing methods to speed up testing and promote at-home testing. Read this article to learn how these tests work and expand your knowledge on COVID-19.
Read Also : Should My Child Get The COVID-19 Vaccine?